
When you transform the conductor into turns, then we get flux linkage λ as NΦ. The flux linkages link the magnetic flux with the turns of the conductor. The unit magnetic flux density is weber m 2 or Tesla. The magnetic flux density is usually represented by B. The total perpendicular magnetic flux per unit area gives us the magnetic flux density. What is magnetic flux density?Īs the name suggests, the magnetic flux density provides the density. Phi is used to represent the magnetic flux. Magnetic flux gives us the number of the magnetic field that passes through a given surface. The flux provides us with the number of anything passing through anything. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) What is magnetic flux? So, using the above formula, we find magnetic flux with an angle. It was all about magnetic flux vs magnetic flux linkage. Θ is the angle the magnetic field makes with the plane. Substituting this formula in the above formula of flux linkage, we get: The formula of magnetic flux is given by Φ = B A cos Φ. Now, if we substitute the formula of magnetic flux in the flux linkage formula, we will get magnetic flux linkage with angle. The flux linkage formula, as we have seen, is NΦ. Ɛ = -N dΦ/dt Magnetic flux linkage formula with angle Here we can see the equation difference of magnetic flux vs magnetic flux linkage. This law provides us with the equation of magnetic flux linkage. What is magnetic flux linkage equation?Īccording to Faraday’s Law, the change in magnetic flux linkage induces the emf, i.e., electromotive force. That is why the total magnetic flux becomes zero through a closed surface. This is because, through a closed surface, the number of magnetic field lines going in will be equal to the total magnetic lines going out.

It states that the flux through a closed surface is always equal to zero. Λ= N B A What is the magnetic flux through a closed surface?Īs per the Gauss Law of magnetism, we get the magnetic flux through a closed surface. The loop of the coil is the surface of magnetic flux linkage through which flux is passed.įor the surface with area A, the magnet flux linkage becomes:
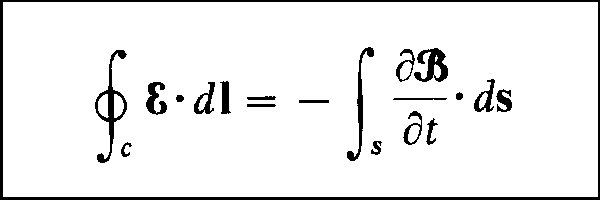
Many consider it to be equal to magnetic flux, but in actuality, it is the extension of the magnetic flux. The flux linkage is often confused with magnetic flux. Where the conductors are thin wires, self-inductance still depends on the wire radius and the distribution of the current in the wire.Image Credit: Wikipedia What is magnetic flux linkage surface?
Magnetic flux formula skin#
Where high frequency currents are considered, with skin effect, the surface current densities and magnetic field may be obtained by solving the Laplace equation. Many important cases can be solved using simplifications. In the most general case, inductance can be calculated from Maxwell's equations. It is customary to use the symbol L radians or 90 degrees, showing that in an ideal inductor the current lags the voltage by 90°. The term inductance was coined by Oliver Heaviside in May 1884. It typically consists of a coil or helix of wire. An electronic component designed to add inductance to a circuit is called an inductor. It is a proportionality factor that depends on the geometry of circuit conductors and the magnetic permeability of nearby materials. Inductance is defined as the ratio of the induced voltage to the rate of change of current causing it. This is stated by Lenz's law, and the voltage is called back EMF. This induced voltage created by the changing current has the effect of opposing the change in current. From Faraday's law of induction, any change in magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) ( voltage) in the conductors, a process known as electromagnetic induction. The field strength depends on the magnitude of the current, and follows any changes in current. The flow of electric current creates a magnetic field around the conductor. Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
